
If you are a business owner who regularly buys or sells goods across borders, you are probably familiar with letters of credit (LCs).
LCs are one of the most widely used payment methods in international trade, as they provide a guarantee of payment from a bank to the seller and a guarantee of delivery from the seller to the buyer. Getting paid fully and on time for every sale means carefully choosing the right payment methods.
Though LCs stand as one of the most secure tools for international traders, their application represents less than 10% of global trade. The complexity and cost associated with LCs can be daunting, especially for smaller transactions. Hence the declining use of LCs prompts the exploration of other secure payment mechanisms like Cedar Money
Cedar Money presents a simpler, more cost-effective solution. It facilitates direct, secure payments without the need for complex documentation or intermediaries.
To facilitate a comprehensive understanding, this article will dissect the intricacies of LCs, highlighting their traditional role in trade and the associated challenges. It will then introduce Cedar Money as a streamlined, accessible alternative, detailing its operation, benefits, and how it contrasts with LCs in terms of ease of use and cost-effectiveness. Finally, we will compare and contrast Cedar Money and LCs, and provide some recommendations and tips for choosing the best payment method for your needs.
What are LCs and how do they work?
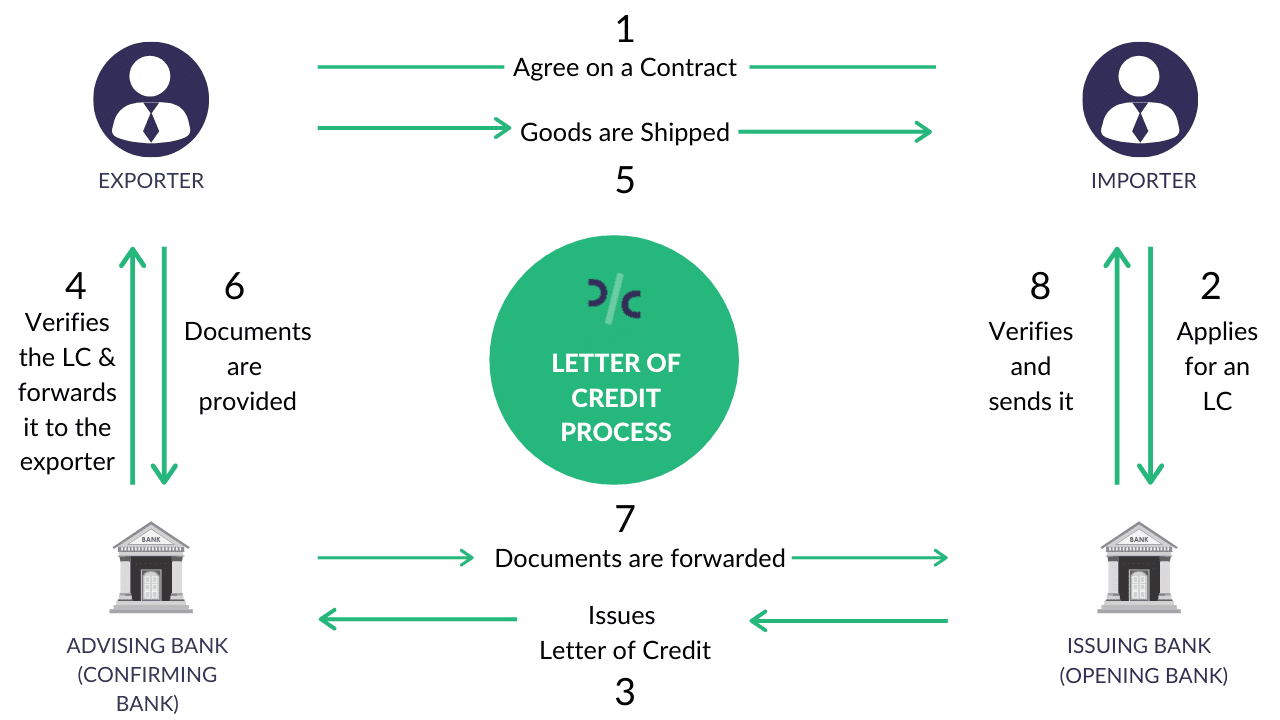
Image Source: Drip Capital
Letters of credit (LCs) are one of the most secure instruments available to international traders. An LC, also known as a documentary credit, is a contractual agreement whereby the issuing bank (the buyer’s bank), acting on behalf of its customer (the buyer), promises to make payment to the beneficiary (the seller) against the receipt of “complying” stipulated documents.
These documents typically include a commercial invoice, a bill of lading, a certificate of origin, and an inspection certificate. The documents must match the terms and conditions of the LC, and they must be presented within a specified timeframe. The issuing bank will usually use intermediary banks to facilitate the transaction and make payment to the seller.
The main advantage of using an LC is that it provides security and certainty to both parties in a trade transaction. The seller is assured of receiving payment from a reputable bank, as long as they comply with the documentary requirements. The buyer is assured of receiving the goods as agreed with the seller, as the payment is conditional on the presentation of the documents. An LC also reduces the risk of non-payment or non-delivery due to political, economic, or legal factors in the buyer’s or seller’s country.
However, LCs also have several disadvantages and challenges, such as:
High costs: LCs involve multiple fees and charges, such as issuance fees, advising fees, confirmation fees, negotiation fees, and amendment fees. These fees vary depending on the bank, the country, and the amount of the LC. According to a study by the European Bank for Reconstruction and Development (EBRD), the average cost of an LC is 1.15% of the transaction value, and it can range from 0.5% to 3%. These costs can reduce the profit margin and competitiveness of the seller, and they can also be passed on to the buyer, increasing the price of the goods.
Complexity: LCs involve a lot of paperwork and documentation, which can be tedious and error-prone. A minor discrepancy or inconsistency in the documents can result in the rejection or delay of the payment by the bank. According to the EBRD, the discrepancy rate of LCs is around 50%, meaning that half of the LCs presented to banks are not accepted at first sight. This can cause frustration and disputes between the parties, and it can also affect the delivery and quality of the goods.
Time-consuming: LCs can take a long time to process and settle, as they require the verification and approval of multiple parties and documents. According to the EBRD, the average processing time of an LC is 16 days, and it can range from 5 to 30 days. This can affect the cash flow and liquidity of the seller, and it can also delay the shipment and receipt of the goods by the buyer.
Traditional Payment Alternatives to Letters of Credit
In addition to the Letter of Credit, various traditional payment methods exist for purchasing goods. It’s recommended to assess these methods during or before contract negotiations to find a mutually advantageous option for both the seller and the buyer. Below, we outline six widely used methods:
1. Advance payment/Cash in Advance (CIA): In this method, the buyer makes payment upfront before the goods are shipped. This provides a level of security for the seller but might pose a risk for the buyer as they pay before receiving the goods.
2. Open Account: This is a more trusting arrangement where the seller ships the goods and allows the buyer a specified period to make the payment. It relies heavily on trust between the buyer and seller.
3. Documentary Collections: This involves using banks to handle the payment and documents. The seller sends shipping documents to their bank, which forwards them to the buyer’s bank along with payment instructions. The buyer can receive the documents upon payment.
4. Bank Guarantees: Instead of a letter of credit, a buyer can use a bank guarantee, which is a commitment by a bank to pay the seller if the buyer fails to fulfil the terms of the agreement.
5. Escrow account arrangements: An independent third party (escrow service) holds the payment until the buyer receives and accepts the goods. Once the buyer approves, the payment is released to the seller.
6. Consignment: In a consignment arrangement, the seller sends the goods to the buyer, but the seller retains ownership until the buyer sells the goods. Payment is then made to the seller based on the actual sales.
Cedar Money: A Smarter Way to Pay for Goods Internationally
Cedar Money is a digital payment solution that transforms the way businesses transfer payments across borders. The payment solution operates on a blockchain-based platform that enables fast, secure, and transparent transactions between buyers and sellers, without the need for intermediaries or complex documentation. Cedar Money offers the following features, functions, and benefits:
Simplicity: Cedar Money is easy to use and access. All you need is a smartphone or a computer with an internet connection. You can sign up for a Cedar Money account in minutes and start sending and receiving money instantly. You do not need to deal with any paperwork or documentation, as Cedar Money verifies your identity and the details of the transaction electronically. You can also track the status and history of your transactions on your Cedar Money dashboard, and you can receive notifications and alerts on your phone or email.
Affordability: Cedar Money is cost-effective and competitive. Cedar Money charges a low and flat transaction fee of 0.5% of the transaction value, regardless of the amount, the currency, or the country. There are no hidden fees or charges, and you can see the exact amount and exchange rate of your transaction before you confirm it. Cedar Money also offers favourable and transparent exchange rates, based on the market rates and the supply and demand of the currencies. You can save up to 80% on the costs of cross-border payments compared to using LCs or other traditional methods.
Speed: Cedar Money is fast and efficient. Transactions are processed and settled within minutes, as they do not require the involvement or approval of any third parties or intermediaries. Cedar Money uses a distributed ledger technology (DLT) that records and validates the transactions on a network of nodes, ensuring the accuracy and integrity of the data. It also uses smart contracts that execute the transactions automatically based on the predefined terms and conditions agreed by the parties. You can receive or send money in real-time, and you can also expedite the shipment and delivery of the goods.
Security: Cedar Money is safe and reliable. Cedar Money transactions are encrypted and protected by advanced cryptographic algorithms, ensuring the confidentiality and authenticity of the data. The payment platform also uses a multi-signature system that requires the consent and verification of both parties before releasing the funds, ensuring the accountability and trustworthiness of the parties. Cedar Money also complies with the highest standards and regulations of the financial industry, such as the Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and the Know Your Customer (KYC) policies, ensuring the legality and legitimacy of the transactions.
How does Cedar Money compare and contrast with LCs?
Cedar Money and LCs are two different payment methods that can be used for purchasing goods across borders. However, they have significant differences in terms of cost, speed, convenience, and risk. The table below summarizes the main pros and cons of each method:
| Method | Pros | Cons |
| LCs | - Provide security and certainty to both parties | - High costs |
| - Reduce the risk of non-payment or non-delivery | - Complexity | |
| - Suitable for large and long-term transactions | - Time-consuming | |
| Cedar Money | - Low and flat transaction fee | - Require internet access and digital literacy |
| - Fast and efficient processing and settlement | - Depend on the availability and stability of the DLT network | |
| - Easy and convenient to use and access | - Not widely accepted or recognized by some banks or authorities | |
| - Secure and transparent transactions | - Suitable for small and medium-sized transactions |
As you can see, Cedar Money has many advantages over LCs, especially for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) that need to make frequent and low-value transactions.
Using the payment solution can help SMEs save money, time, and hassle and improve their cash flow, profitability, and competitiveness.
However, Cedar Money also has some limitations and challenges, such as the need for internet access, digital literacy, and dependence on the DLT network.
Additionally, Cedar Money’s expansive reach across Europe, the UK, Africa, the Middle East, and parts of Asia necessitates adapting to diverse market-specific regulations and cultural norms.
Read Also: How to start a Dropshipping business in Nigeria
Choosing the Ideal Payment Method for Trade
Selecting the right payment method for your import/export business involves evaluating your needs, the transaction’s risk level, and trust between parties. Consider these steps for an optimal choice:
Evaluate the transaction’s risk and trust: For new or uncertain trade partners, especially from high-risk countries, opt for more secure methods like Letters of Credit (LC) or cash in advance. For established partners from stable regions, open accounts or documentary collections might suffice.
Weigh each method’s costs against its benefits: Secure methods like LCs provide safety but come with higher fees and complexity. Conversely, open accounts are cheaper and simpler but riskier. Aim for a balance that maximises value.
Stay updated on payment innovations: The payment sector is continually evolving, offering new solutions to streamline and secure international trade transactions.
In Conclusion
With Cedar Money, businesses can make international payments efficiently, leveraging favourable exchange rates and lower transaction fees. We recommend that you explore the features and benefits of Cedar Money, and compare it with other payment methods, to find the best fit for your business. You can visit the official website to start your journey to seamless cross-border payments.
